똑같은 삽질은 2번 하지 말자
Spring Boot 개념다지기 No.7( @Profile(프로파일),Logger(로깅) ) 본문
@Profile(프로파일)
@Profile 애노테이션은 어디에?
어떤 특정한 Bean 설정을 하고 싶을때,
application.properties에
어떤 프로파일을 활성화 할 것인가? 를 정할 수 있는데
spring.profiles.active = prodprod 라는 프로파일을 활성화 시킨다.
다음은 자바 코드로 활성화한 프로파일로 스프링 시큐리티 환경설정
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@Profile("Prod")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public static class LessPermissiveSecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final JwtTokenProvider jwtTokenProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity
.httpBasic()
.disable()
.csrf()
.disable()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.addFilterBefore(new JwtTokenFilter(jwtTokenProvider), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@Profile("Test")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public static class InsecureSecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
//@formatter:off
httpSecurity
.httpBasic()
.disable()
.csrf()
.disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().permitAll()
;
//@formatter:on
}
}
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
따로 프로파일용 프로퍼티를 정의하는 것도 가능하다.
ex) application-{profile이름}.properties
이렇게 만들고 따로 따로 설정파일을 만드는것도 가능함.
로깅
SLF4j 는 로깅 퍼사드(추상화한거) 실제로 로그를 찍는 역할이 아니고,
로거로 JUL, Log4J2, Logback 이 있다. 로깅 퍼사드를 씀으로써 로거 쉽게 교체가능하게 함
부트는 기본적으로 Commons Logging 을 쓴다고 한다.
but 결국 로그는 Logback 로거로 찍힌다.. 음 그냥 그렇게 알자..
아 그리고 디버깅레벨로 로그를 찍히게 하고 싶으면 간단한 방법이 있는데
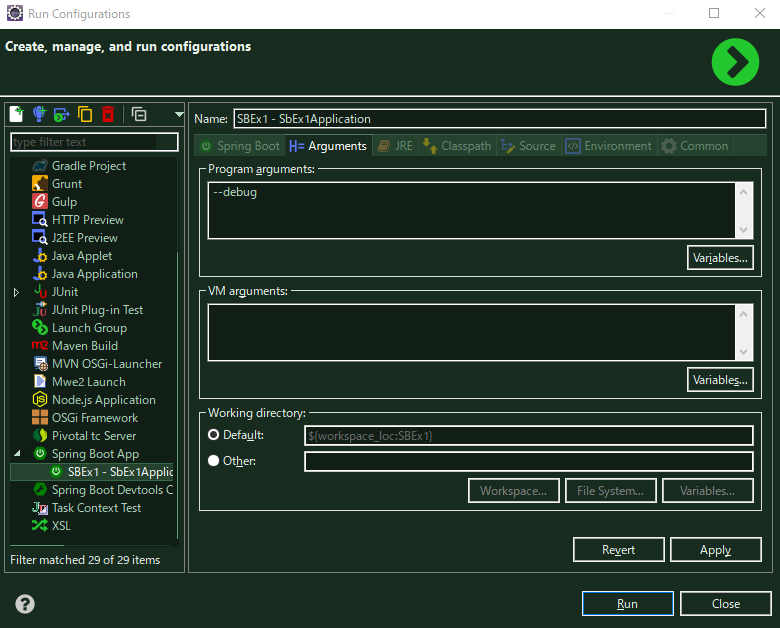
이클립스인데 저기 Program arguments 에 --debug를 주면 된다.
스프링 부트에서는 로깅 설정을 자동적으로 지원합니다.
다음과 같이 slf4j 로깅 파사드( 로깅 모듈을 추상화한 것 )를 통해 logback 을 기본적으로 지원하고 있죠.
@Component
public class AppRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
// slf4j 로깅 파사드를 통해 logback 로깅 모듈을 지원
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AppRunner.class);
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
logger.info("=============");
logger.info("This is Spring Boot App");
logger.info("=============");
}
}
application.properties
- 컬러 출력: spring.output.ansi.enabled
- 파일 출력: logging.file 또는 logging.path
- 로그 레벨 조정: logging.level.패지키 = 로그 레벨
# 콘솔 창에 출력되는 로깅 메세지를 색으로 구분해서 출력
spring.output.ansi.enabled=always
# 로그 메세지가 저장되는 로그 디렉터리
logging.path=logs
# logging.level.{패키지 경로}를 통해 로깅 레벨을 결정할 수 있슴
logging.level.com.tutorial.springboot=DEBUG
만일 logback을 사용하지 않고 다른 로깅 모듈로 바꾸고 싶을 때는 pom.xml에 다음과 같이 logback 모듈에 대한 의존성을 제거해야 합니다.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
그 다음 log4j 같은 다른 로깅 모듈에 대한 의존성을 추가합니다.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>
왜 쓸까?
logging framework는 로그를 레벨단위로 설정할 수 있어 관리가 용이하다는 점
몇 가지 설정을 통해서 로그를 파일로 저장이 가능하다는점등
다양한 편리 기능을 제공
'Spring > Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Boot 개념다지기 No.8(테스트) (0) | 2020.04.27 |
|---|---|
| Gradle -> Maven (0) | 2020.04.27 |
| Spring Boot 개념다지기 No.6(SpringApplication, 외부설정) (0) | 2020.04.25 |
| Spring Boot 개념다지기 No.5 (0) | 2020.04.25 |
| Spring Boot 개념다지기 No.4 (0) | 2020.04.24 |



