똑같은 삽질은 2번 하지 말자
Typescript + Vue (Vuex) No.2 본문
Typescript 로 마이그레이션 하면서 기록하고 싶은것들 2
vuex-module-decorator나 다른 타입 라이브러리들을 안쓰고 vuex에 타입시스템을 적용시키며 타입 추론이 되게하는 방법이다.
(vue3가 되면 코어에 타입스크립트를 잘 씌울 수 있게 대응해 줬기때문에 vue2에서는 이렇게 한다는 느낌으로다가 그냥 가볍게 보자. )
1. state에 타입을 씌우기
store/index.ts
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex, { StoreOptions } from "vuex";
import { state, RootState } from "./state";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store: StoreOptions<RootState> = {
state: state,
};
export default new Vuex.Store(store);store/state.ts
import { NewsItem } from "@/api";
export const state = {
news: [] as NewsItem,
};
export type RootState = typeof state;하지만 이렇게해도 타입추론은 안된다.
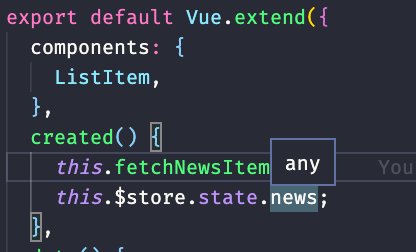
이건 vuex의 vue.d.ts 파일을 직접 건들면 추론이 이루어 질 수 있다. (실무에서는 쓸 수 있는 방법이 아니므로 추후에 대안을 쓰겠다.)
node_modules/vuex/types/vue.d.ts
import { RootState } from "@/store/state";
import Vue, { ComponentOptions } from "vue";
import { Store } from "./index"; // 나의 Store
declare module "vue/types/options" {
interface ComponentOptions<V extends Vue> {
store?: Store<RootState>; // 삽입
}
}
declare module "vue/types/vue" {
interface Vue {
$store: Store<RootState>; // 삽입
}
}
2. mutation에 타입을 씌우기
mutation도 역시 vuex의 vue.d.ts에 타입을 알려주지 않는이상 타입추론이 일어나지 않는다.
mutations의 타입을 곁들인 타입파일이 필요한 시점이다.
store/mutations.ts
import { NewsItem } from "@/api";
import { RootState } from "./state";
export enum MutationTypes {
SET_NEWS = "SET_NEWS",
}
export const mutations = {
[MutationTypes.SET_NEWS](state: RootState, news: NewsItem[]) {
state.news = news;
},
};
export type Mutations = typeof mutations;여기서 [MutationTypes.SET_NEWS] -> 이 부분 좀 의아해 할 수 있는 부분인데, 상수화하는게 나중에 타입추론에서 이점을 얻을 수 있기때문에 상수화를 했고, 공식문서에서도 추천하고 있는 방법이다. ([]이 문법은 es 6의 computed property name)
*computed property name ? 표현식(expression)을 이용해 객체의 key 값을 정의하는 문법
const name = "희원곽"
const age = 30
const obj = {
[name]: "이름",
[age]: "나이",
}
store/index.ts
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex, { StoreOptions } from "vuex";
import { mutations } from "./mutations";
import { state, RootState } from "./state";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store: StoreOptions<RootState> = {
state: state,
mutations: mutations,
};
export default new Vuex.Store(store);store/type.ts
import { CommitOptions, Store } from "vuex";
import { Mutations } from "./mutations";
import { RootState } from "./state";
type MyMutations = {
commit<K extends keyof Mutations, P extends Parameters<Mutations[K]>[1]>(
key: K,
payload?: P,
options?: CommitOptions
): ReturnType<Mutations[K]>;
};
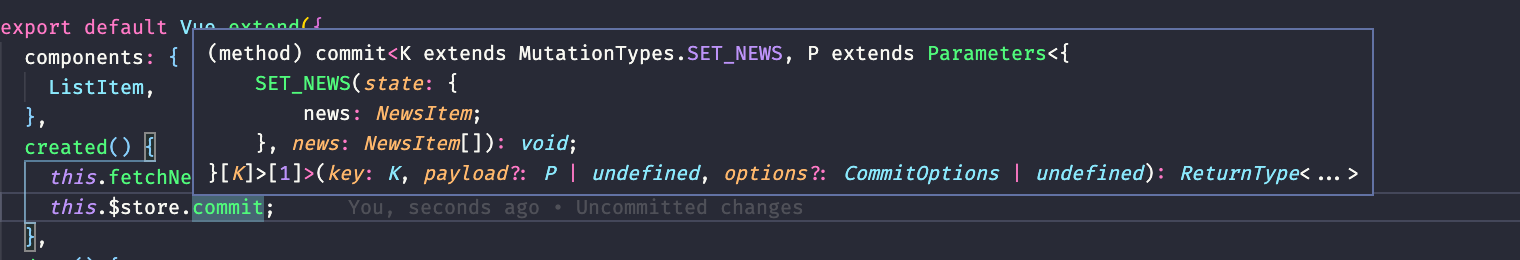
export type MyStore = Omit<Store<RootState>, "commit"> & MyMutations;Omit<Store<RootState>, "commit"> & MyMutations -> 제네릭의 두번째 param "commit"의 제외한 나머지 타입을 전부 받아들이고 내가 정의한 MyMutations가 commit 타입으로써 정의되는 것 이다.
이제 MyStore를 삽입시키면 된다.
node_modules/vuex/types/vue.d.ts
/**
* Extends interfaces in Vue.js
*/
import { RootState } from "@/store/state";
import { MyStore } from "@/store/type";
import Vue, { ComponentOptions } from "vue";
import { Store } from "./index";
declare module "vue/types/options" {
interface ComponentOptions<V extends Vue> {
store?: MyStore;
}
}
declare module "vue/types/vue" {
interface Vue {
$store: MyStore;
}
}
3. actions에 타입을 씌우기 & store의 타입추론이 잘 이루어지게 프로젝트 레벨의 *.d.ts 정의하기
store/actions.ts
import { fetchNews, NewsItem } from "@/api";
import { ActionContext } from "vuex";
import { Mutations, MutationTypes } from "./mutations";
import { RootState } from "./state";
export enum ActionTypes {
FETCH_NEWS = "FETCH_NEWS",
}
export type MyActionContext = {
commit<K extends keyof Mutations>(
key: K,
payload: Parameters<Mutations[K]>[1]
): ReturnType<Mutations[K]>;
} & Omit<ActionContext<RootState, RootState>, "commit">;
export const actions = {
async [ActionTypes.FETCH_NEWS](
context: MyActionContext,
payload?: NewsItem[]
): Promise<NewsItem[]> {
const { data } = await fetchNews();
context.commit(MutationTypes.SET_NEWS, data);
return data;
},
};
export type Actions = typeof actions;1. actions 이름을 상수화
2. context 타입을 내가 정의한 mutations로 ActionContext commit 부분만 커스텀해서 Omit해준다.
3. actions에 context타입에 커스텀한 ActionContext를 씌워준다.
store/type.ts
import { CommitOptions, DispatchOptions, Store } from "vuex";
import { Actions } from "./actions";
import { Mutations } from "./mutations";
import { RootState } from "./state";
type MyMutations = {
commit<K extends keyof Mutations, P extends Parameters<Mutations[K]>[1]>(
key: K,
payload?: P,
options?: CommitOptions
): ReturnType<Mutations[K]>;
};
type MyActions = {
dispatch<K extends keyof Actions>(
key: K,
payload?: Parameters<Actions[K]>[1],
options?: DispatchOptions
): ReturnType<Actions[K]>;
};
export type MyStore = Omit<Store<RootState>, "commit" | "dispatch"> &
MyMutations &
MyActions;지금까지 한 타입들을 정리하여 store/type.ts에 정의 내 Store의 타입을 정의한다.
types/project.d.ts
import Vue from "vue";
import { MyStore } from "../store/type";
// TODO: node_module/vuex/type/vue.d.ts 파일을 삭제해줘야 아래 타입이 정상 추론된다.
declare module "vue/types/options" {
interface ComponentOptions<V extends Vue> {
store?: MyStore;
}
}
declare module "vue/types/vue" {
interface Vue {
$store: MyStore;
}
}타입정의파일을 만들어
tsconfig.json에 내가 정의한 타입정의파일을 포함시켜 type intelligence가 읽어들이게 해준다.
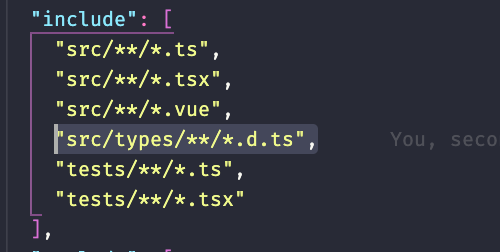
node_modules/vuex/type/vue.d.ts 파일을 삭제시켜주면 내가 정의한 project.d.ts로 $store의 타입추론이 이루어지는걸
알 수 있다.

참고(declare module)
https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/declaration-merging.html#module-augmentation
Documentation - Declaration Merging
How merging namespaces and interfaces works
www.typescriptlang.org
